Two-Pointer Sliding Window Algorithm
One of the most common approaches to solve many algoritm problems is to apply some type of 2-Pointer approach. The 2-Pointer approach is used to search over a list (or multiple list) in such a way that the time complexity can be minimised. Consider the following problem:
Problem Statement: Given an array of positive integers and a positive target integer, return the minimal length of a contiguous sub-array of which the sum is greater than or equal to the target.
This article visually explains how we can use a two-pointer algorithm with a sliding window to solve this problem with \(O(n)\) time complexity.
One solution to solve this kind of problem is to use the 2-Pointer approach with a sliding window. The diagram below illustrates this solution with the inputs nums = [1,2,2,3,3,2,3,4,1,2] and target = 7.
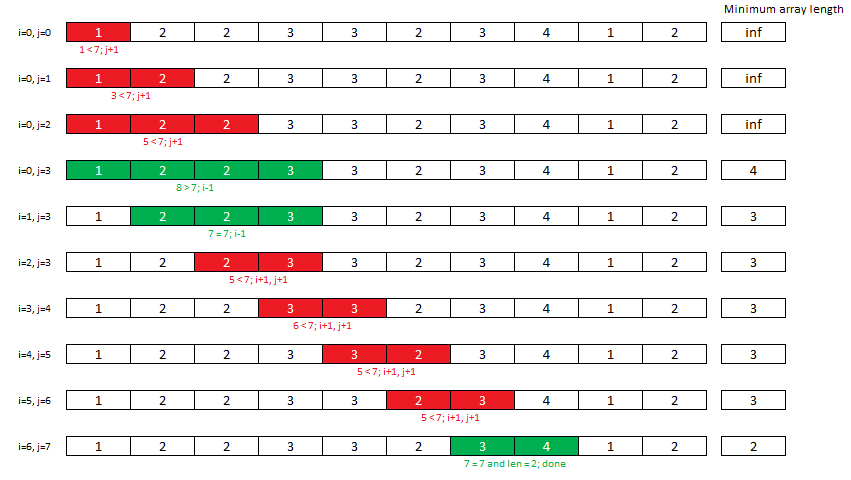
Using a sliding window ensures that we do not check sub-arrays which we know are larger than the smallest sub-array we have found so far. We can end our search when either the length of the sub-array is equal to two (since the only better solution is if the target is in the array) or we have traversed the whole array.
def minSubArrayLen(nums, target):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:type target: int
:rtype: int
"""
# Iterators i:left pointer and j:right pointers
i, j = 0, 0
# Save the length so that we only do the calulation once
length = len(nums)
# define the minimum array length "min_array" and sum of current array "s"
min_array = float("inf")
s = nums[0]
# Check if target is in the array
if target in nums:
return 1
# Otherwise check if the length of the array is 1
elif length == 1:
return 0
# Otherwise start searching through the array
else:
# While the right pointer is still in the array (min_array = 2 means we cant to any better)
while j < length and min_array > 2:
# find the first sub array which meets the condition
if i == 0 and s < target:
j += 1
if j < length:
s += nums[j]
# Once we find an array then save the length of it
elif s >= target:
min_array = j - i + 1
s -= nums[i]
i += 1
# If found an array and current array does not meet the condition
# then we can shift both sides of the array to check if we can do better
elif s < target:
j += 1
if j < length:
s += nums[j]
s -= nums[i]
i += 1
# Return the answer is an array has been found
if min_array == float("inf"):
return 0
return min_arrayEvaluating this function below
minSubArrayLen(nums = [1,2,2,3,3,2,3,4,1,2], target = 7)The result is 2 as expected.
